Articles by Aaron Fagan
This course will address both the geometry and rating of involute splines of various types
Read More
Recent Cutting Tools from Kennametal, Star SU, and Seco Offer Improved Tool Life and Precision
Reliable cutting tools are essential to production-process efficiency
Read More
Quality Assurance Stakeholders Meet at Control 2022
Gleason and Klingelnberg unveil new quality assurance technologies
Read More
KISSsoft for Gear Manufacturing
Software integrates design, production, and metrology as a holistic process
Read More
Liebherr Helps Customers Master E-mobility Gear Challenges
High quality demands puts high demands on integrated gear-production processes
Read More
Solvay Specialty Polymers for High-Performance Plastic Gears
Thermoplastic injection-molded parts in automotive applications is growing and proving significant reductions in NVH issues
Read More
Versatile Hobbing Solutions from Affolter, Helios and Nidec
Improved productivity and reduced processing costs drive innovation
Read More
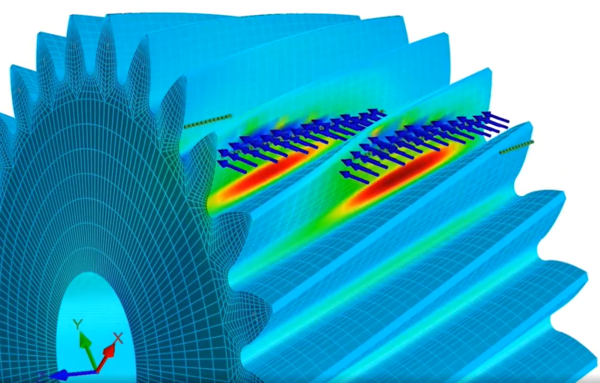
The Role of Virtual Prototyping in Gear System Design and Manufacturing for E-Mobility
The combination of full-system simulation and gear-machining simulation ensures manufacturability
Read More
The Evolution of QuesTek's Ferrium C64 for Additive Manufacturing
The unique processing conditions of 3D-printed metal gears have come a long way
Read More