Features
Current state-of-the-art and developing trends
Read More
Internal Gearing, Deburring, Honing and the Advancement of Robotic Cells
Examines the changing face of machine operation today
Read More
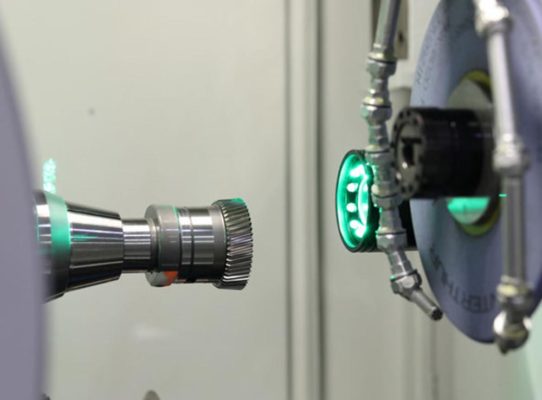
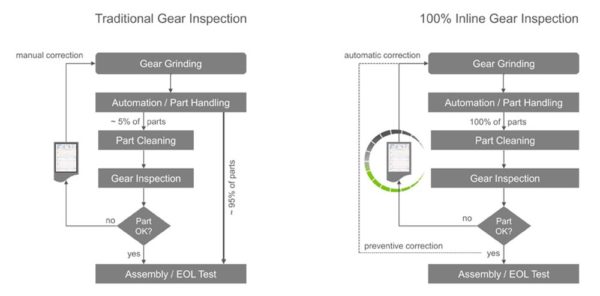
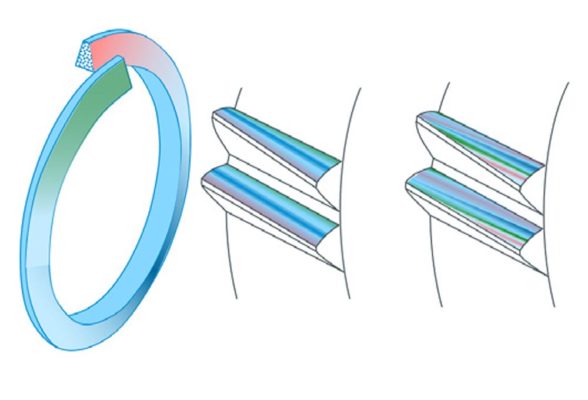
Noise Analysis for e-Drive Gears and In-Process Gear Inspection
Ensure optimum quality in a fraction of the time
Read More
Technology Advances for Continuous Generating Gear Grinding in EV and More
Meeting the challenges of gear grinding with innovative abrasive technology that improves gear efficiency and quality
Read More
Maximizing Wind Turbine Gearbox Performance with Advanced Engineering Simulation
ZF Wind Power achieves wind turbine gearbox efficiency and reliability through Siemens Simcenter Solutions
Read More
Take Control of Quenching
Press quenching technology for more hardening consistency, improved operator efficiency, and faster throughput of a wide range of gears and other close-tolerance cylindrical components
Read More
What’s Happening in Heat Treating?
Acquisitions, retirements and facility expansions highlight start to 2023
Read More
The Secrets to Implementing Lights-Out Machining
Making a whole day productive requires strategy not staffing
Read More